RVTK Example: Input/Output.
The result of example described in previous sections looks like:
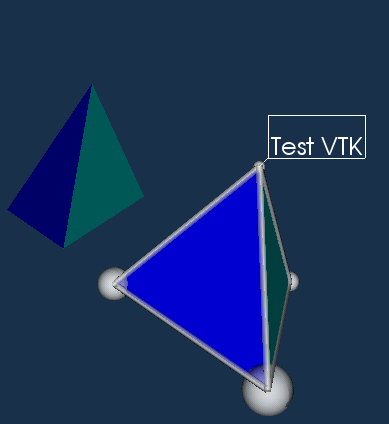
The routine to get png (or any other image format) is to use one
special case of a filters - exporters. They have input but no output
except file one. To get the hardcopy we should first run a filter which
convert the content of rendering window into vtkImageData and then put
this data into image file.
vtkWindowToImageFilter()->f
f$SetInput(.vtk)
f$Modified()
vtkPNGWriter()->png
png$SetFileName("example2.png")
png$SetInput(f$GetOutput())
png$Write()
The result is not much different from the result we would get by taking
a screenshot of rendering window (ImageMagick would do this job OK). To
get scalable output in vector format (ps or pdf) the special case of
exporter should be used - GL2PS one. The corresponding code is not built
by default in VTK so to enable it you first have to take special care
to check it in ccmake while configuring VTK and then install RVTK.GL2PS
R-package.
library(RVTK.GL2PS)
vtkGL2PSExporter()->gp
gp$SetInput(.vtk)
gp$SetSortToBSP()
gp$SetFileFormatToPDF()
gp$SetFilePrefix("example2")
gp$Write()
SetSortToBSP() method enables more careful calculation of intersections
which leads to better image quality. The format of output (as well as
result file extension) is controlled by methods
SetFileFormatToPDF()/SetFileFormatToPS().SetFilePrefix() - is the name
of the result file without extension. If you look into result file you will understand why
GL2PS considered alpha. Although for simple models it is applicable very
well but for more complicated one it fails due to drawbacks of
postscript language (it was not designed for 3D rendering). In our
example the opacity information is not handled by converter.
